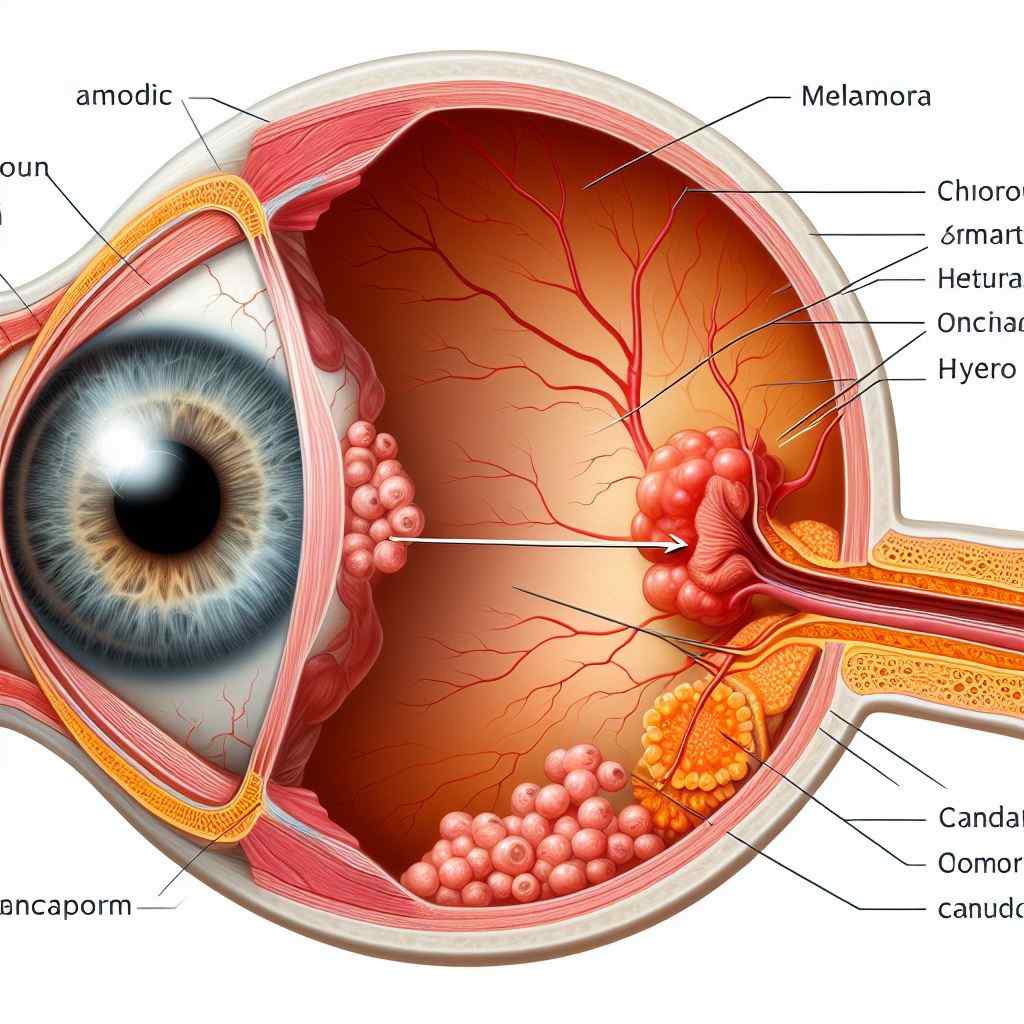
Navigating Choroidal Melanoma: Insights into Diagnosis and Treatment
Choroidal melanoma, albeit rare, poses significant challenges in ophthalmic oncology due to its potential for metastasis and vision-threatening complications. This article provides a comprehensive overview of choroidal melanoma, encompassing its epidemiology, clinical features, diagnostic modalities, treatment options, and recent advancements in the field.
Introduction: Choroidal melanoma represents the most common primary intraocular malignancy in adults, arising from melanocytes within the choroid. Despite its infrequency, choroidal melanoma necessitates vigilant surveillance and prompt intervention to mitigate the risk of metastasis and preserve visual function.
Epidemiology: Choroidal melanoma predominantly affects individuals in their fifth to seventh decades of life, with a slight predilection for Caucasians. While relatively rare, choroidal melanoma accounts for a significant proportion of ocular malignancies, posing a formidable challenge to ophthalmic clinicians and oncologists.
Clinical Features: Choroidal melanoma typically manifests as an asymptomatic choroidal mass, often incidentally detected on routine ophthalmic examination or through the evaluation of visual symptoms such as blurred vision, metamorphopsia, or visual field defects. Characteristic features include orange pigment, subretinal fluid, and acoustic hollowness on ultrasonography.
Diagnostic Modalities: The diagnosis of choroidal melanoma relies on a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Ancillary diagnostic modalities such as ultrasonography, fundus autofluorescence, optical coherence tomography (OCT), fluorescein angiography, and indocyanine green angiography aid in delineating tumor characteristics and guiding therapeutic decisions.
Treatment Options: The management of choroidal melanoma encompasses a spectrum of therapeutic modalities tailored to tumor size, location, and patient-specific factors. Treatment options include plaque brachytherapy, proton beam radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, surgical resection, and observation with periodic monitoring. Multidisciplinary collaboration is essential in determining the optimal treatment approach for each patient.
Recent Advancements: Recent advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of choroidal melanoma have revolutionized our approach to this challenging malignancy. Innovations in imaging technology, such as enhanced depth imaging OCT and wide-field fundus photography, have facilitated early detection and accurate tumor characterization. Additionally, targeted therapies and immunotherapies hold promise in the management of metastatic disease and may offer new avenues for personalized treatment.
Conclusion: In conclusion, choroidal melanoma represents a formidable adversary in ophthalmic oncology, necessitating a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and management. By leveraging advances in imaging technology, refining treatment algorithms, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we can optimize outcomes for patients with choroidal melanoma and advance our understanding of ocular malignancies.
Links:


