Understanding Orbital Cellulitis: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract: Orbital cellulitis is a serious ophthalmic condition characterized by infection and inflammation of the tissues surrounding the eye. This article provides a thorough examination of orbital cellulitis, covering its etiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, management strategies, and recent advancements in treatment. By elucidating the complexities of this condition, ophthalmologists can enhance their clinical acumen and optimize patient outcomes.
Introduction: Orbital cellulitis poses a significant clinical challenge due to its potential for causing vision-threatening complications and systemic sequelae. Understanding the pathophysiology and management principles of this condition is crucial for timely intervention and favorable patient outcomes.
Etiology: Orbital cellulitis often arises secondary to the spread of infection from adjacent structures, such as the paranasal sinuses or eyelids, commonly following sinusitis or trauma. Bacterial pathogens, notably Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species, are frequently implicated, although fungal etiologies should also be considered, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
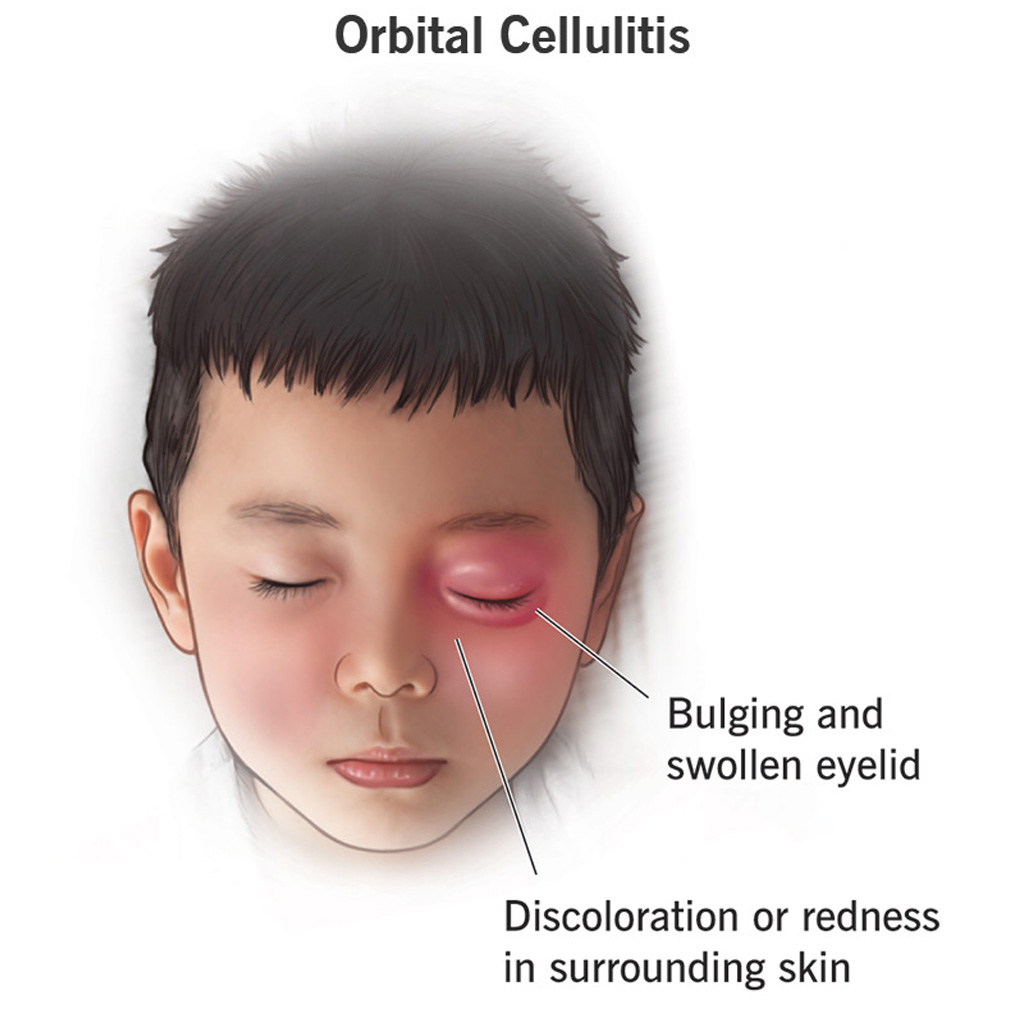
Clinical Presentation: Patients with orbital cellulitis typically present with periorbital pain, eyelid swelling, proptosis, restricted ocular motility, and systemic signs of infection such as fever and malaise. Severe cases may manifest with vision loss, orbital abscess formation, or even cavernous sinus thrombosis, necessitating urgent intervention.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of orbital cellulitis involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including visual acuity assessment, pupillary examination, extraocular motility testing, and imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to delineate the extent of orbital involvement and identify potential complications.
Management Strategies: Treatment of orbital cellulitis revolves around aggressive antibiotic therapy tailored to cover the likely causative pathogens, often initiated empirically pending culture results. Surgical intervention may be warranted in cases of orbital abscess or subperiosteal abscess to facilitate drainage and alleviate orbital pressure. Close monitoring of clinical progress and response to treatment is essential for guiding management decisions.
Recent Advancements: Recent innovations in the management of orbital cellulitis include the use of novel antibiotic agents with enhanced antimicrobial spectra and reduced resistance profiles, as well as minimally invasive surgical techniques such as endoscopic sinus surgery for addressing underlying sinus pathology. Additionally, advancements in imaging modalities, such as diffusion-weighted MRI, hold promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and prognostication.
Conclusion: Orbital cellulitis represents a significant ophthalmologic emergency requiring prompt recognition and intervention to prevent sight-threatening complications. By staying abreast of the latest developments in diagnosis and treatment, ophthalmologists can effectively manage this condition and optimize patient outcomes.
For further reading and reference:
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) – Orbital Cellulitis Information: https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/orbital-cellulitis-list
- British Oculoplastic Surgery Society (BOPSS) – Orbital Cellulitis Guidelines: https://www.bopss.co.uk/professionals/clinical-guidelines/orbital-cellulitis/


